|
Monday, December 8, 2025
Motivational Speaker Quote | Contact for free
Tuesday, December 2, 2025
APOD Email Removal Request
Cheers.
Greg Tracy
gtracy@gmail.com
https://apodemail.org
Notes:
APOD - M77: Spiral Galaxy with an Active Center
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2025-12-02
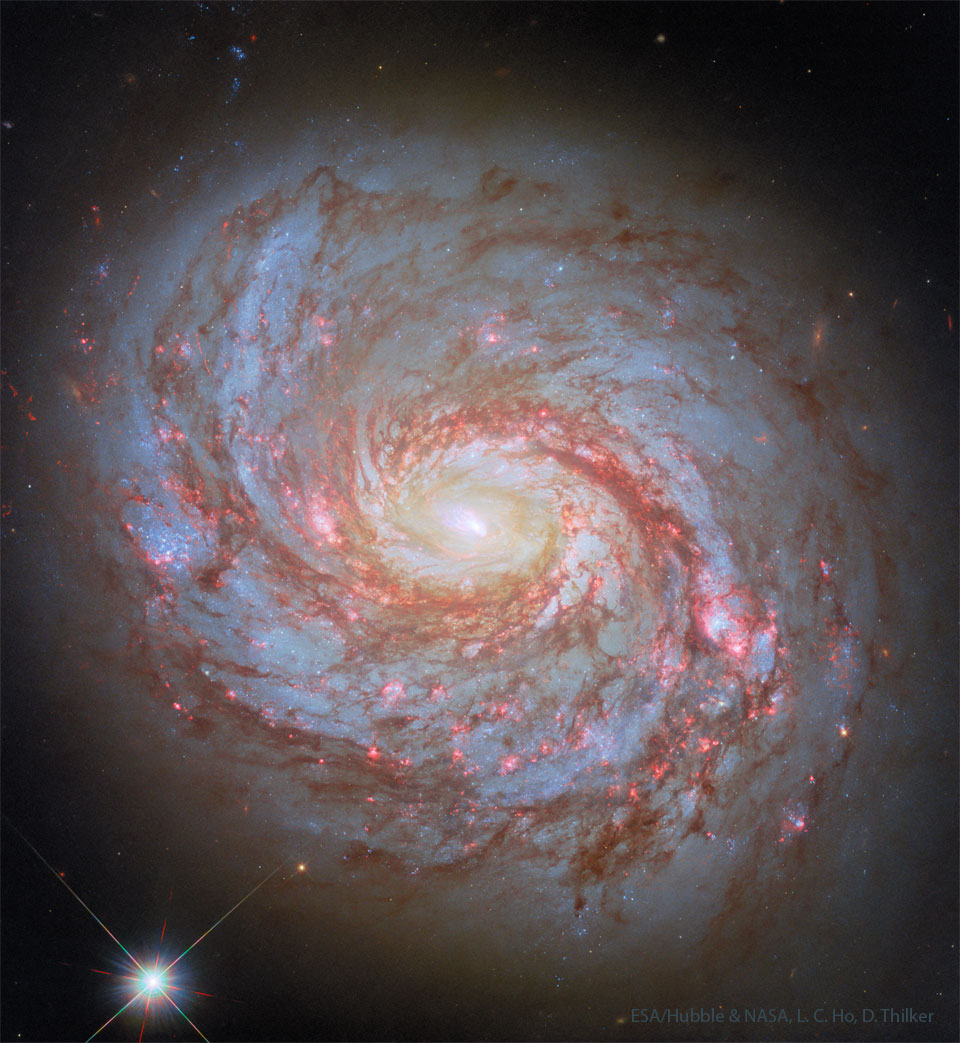

Explanation: What's happening in the center of nearby spiral galaxy M77? The face-on galaxy lies a mere 47 million light-years away toward the constellation of the Sea Monster (Cetus). At that estimated distance, this gorgeous island universe is about 100 thousand light-years across. Also known as NGC 1068, its compact and very bright core is well studied by astronomers exploring the mysteries of supermassive black holes in active Seyfert galaxies. M77's active core glows bright at x-ray, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, and radio wavelengths. The featured sharp image of M77 was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. The image shows details of the spiral's winding spiral arms as traced by obscuring red dust clouds and blue star clusters, all circling the galaxy's bright white luminous center.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org. Unsubscribe
Monday, December 1, 2025
APOD - 3I ATLAS: Tails of an Interstellar Comet
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2025-12-01

Image Credit & Copyright: Victor Sabet & Julien De Winter
Explanation: How typical is our Solar System? Studying 3I/ATLAS, a comet just passing through, is providing clues. Confirmed previous interstellar visitors include an asteroid, a comet, a meteor, and a gas wind dominated by hydrogen and helium. Comet 3I/ATLAS appears relatively normal when compared to Solar System comets, therefore providing more evidence that our Solar System is a somewhat typical star system. For example, Comet 3I/ATLAS has a broadly similar chemical composition and ejected dust. The featured image was captured last week from Texas and shows a green coma, a wandering blue-tinted ion tail likely deflected by our Sun's wind, and a slight anti-tail, all typical cometary attributes. The comet, visible with a telescope, passed its closest to the Sun in late October and will pass its closest to the Earth in mid-December, after which it will return to interstellar space and never return.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org. Unsubscribe
Sunday, November 30, 2025
APOD - The Surface of Titan from Huygens
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit: ESA, NASA, JPL, U. Arizona, Huygens Lander
Explanation: If you could stand on Titan -- what would you see? The featured color view from Titan gazes across an unfamiliar and distant landscape on Saturn's largest moon. The scene was recorded by ESA's Huygens probe in 2005 after a 2.5-hour descent through a thick atmosphere of nitrogen laced with methane. Bathed in an eerie orange light at ground level, rocks strewn about the scene could well be composed of water and hydrocarbons frozen solid at an inhospitable temperature of negative 179 degrees C. The large light-toned rock below and left of center is only about 15 centimeters across and lies 85 centimeters away. The saucer-shaped spacecraft is believed to have penetrated about 15 centimeters into a place on Titan's surface that had the consistency of wet sand or clay. Huygen's batteries enabled the probe to take and transmit data for more than 90 minutes after landing. Titan's bizarre chemical environment may bear similarities to planet Earth's before life evolved.
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Saturday, November 29, 2025
APOD - Moon Games
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit & Copyright: Giorgia Hofer
Explanation: This is not a screen from a video game. Nestled below the treeline, the small mountain church does look like it might be hiding from Moon though. In the well-composed telephoto snapshot, taken on November 23, the church walls are partly reflecting light from terrestrial flood lights. Of course, the Moon is reflecting light from the Sun. At any given time the Sun illuminates fully half of the Moon's surface, also known as the lunar dayside, but on that night only a sliver of its sunlit surface was visible. About three days after New Moon, the Moon was in a waxing crescent phase. The single exposure was captured shortly after sunset in skies near Danta di Cadore, northern Italy, planet Earth.
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Friday, November 28, 2025
APOD - NGC 6888: The Crescent Nebula
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit & Copyright: Greg Bass
Explanation: NGC 6888, also known as the Crescent Nebula, is a about 25 light-years across, a cosmic bubble blown by winds from its central, massive star. This deep telescopic image includes narrowband image data, to isolate light from hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The oxygen atoms produce the blue-green hue that seems to enshroud the nebula's detailed folds and filaments. Visible within the nebula, NGC 6888's central star is classified as a Wolf-Rayet star (WR 136). The star is shedding its outer envelope in a strong stellar wind, ejecting the equivalent of the Sun's mass every 10,000 years. In fact, the Crescent Nebula's complex structures are likely the result of this strong wind interacting with material ejected in an earlier phase. Burning fuel at a prodigious rate and near the end of its stellar life, this star should ultimately go out with a bang in a spectacular supernova explosion. Found in the nebula rich constellation Cygnus, NGC 6888 is about 5,000 light-years away.
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Thursday, November 27, 2025
APOD - Portrait of NGC 1055
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit & Copyright: John Hayes
Explanation: Big, beautiful spiral galaxy NGC 1055 is a dominant member of a small galaxy group a mere 60 million light-years away toward the aquatically intimidating constellation Cetus. Seen edge-on, the island universe spans over 100,000 light-years, a little larger than our own Milky Way galaxy. The colorful, spiky stars decorating this cosmic portrait of NGC 1055 are in the foreground, well within the Milky Way. But telltale pinkish star forming regions and young blue star clusters are scattered through winding dust lanes along the distant galaxy's thin disk. With a smattering of even more distant background galaxies, the deep image also reveals a boxy halo that extends far above and below the central bulge and disk of NGC 1055. The halo itself is laced with faint, narrow structures, and could represent the mixed and spread out debris from a satellite galaxy disrupted by the larger spiral some 10 billion years ago.
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Wednesday, November 26, 2025
APOD - Globular Cluster M15 Deep Field
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit & Copyright: Alvaro Ibanez Perez
Explanation: Stars, like bees, swarm around the center of bright globular cluster M15. The central ball of over 100,000 stars is a relic from the early years of our Galaxy, and continues to orbit the Milky Way's center. M15, one of about 150 globular clusters remaining, is noted for being easily visible with only binoculars, having at its center one of the densest concentrations of stars known, and containing a high abundance of variable stars and pulsars. The featured image of M15 was taken by combining very long exposures -- 122 hours in all -- and so brings up faint wisps of gas and dust in front of the giant ball of stars. M15 lies about 35,000 light years away toward the constellation of the Winged Horse (Pegasus).
Tomorrow's picture: open space
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Tuesday, November 25, 2025
APOD - Comet Lemmon and the Milky Way
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit & Copyright: Lin Zixuan (Tsinghua U.)
Explanation: What did Comet Lemmon look like when it was at its best? One example is pictured here, featuring three celestial spectacles all at different distances. The closest spectacle is the snowcapped Meili Mountains, part of the Himalayas in China. The middle marvel is Comet Lemmon near its picturesque best early this month, showing not only a white dust tail trailing off to the right but its blue solar wind-distorted ion tail trailing off to the left. Far in the distance on the left is the magnificent central plane of our Milky Way Galaxy, featuring dark dust, red nebula, and including billions of Sun-like stars. Comet C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) is already fading as it heads back into the outer Solar System, while the Himalayan mountains will gradually erode over the next billion years. The Milky Way Galaxy, though, will live on -- forming new mountains and comets -- for many billions of years into the future.
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Monday, November 24, 2025
APOD - Apep: Unusual Dust Shells from Webb
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, JWST; Science: Y. Han (Caltech), R. White (Macquarie U.); Image Processing: A. Pagan (STScI)
Explanation: What created this unusual space sculpture? Stars. This unusual system of swirls and shells, known as Apep, was observed in unprecedented detail by NASA's James Webb Space Telescope in infrared light in 2024. Observations indicate that the unusual shape originates from two massive Wolf-Rayet stars orbiting each other every 190 years with each close passes causing a new shell of dust and gas to be expelled. Holes in these shells are thought to be caused by a third orbiting star. This stellar dust dance will likely continue for hundreds of thousands of years, possibly ending only when one of the massive stars runs out of internal nuclear fuel and explodes in a supernova punctuated by a burst of gamma-rays.
Tomorrow's picture: picturesque comet
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Sunday, November 23, 2025
APOD - The Observable Universe
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Illustration Credit & Licence: Wikipedia, Pablo Carlos Budassi
Explanation: How far can you see? Everything you can see, and everything you could possibly see, right now, assuming your eyes could detect all types of radiations around you -- is the observable universe. In light, the farthest we can see comes from the cosmic microwave background, a time 13.8 billion years ago when the universe was opaque like thick fog. Some neutrinos and gravitational waves that surround us come from even farther out, but humanity does not yet have the technology to detect them. The featured image illustrates the observable universe on an increasingly compact scale, with the Earth and Sun at the center surrounded by our Solar System, nearby stars, nearby galaxies, distant galaxies, filaments of early matter, and the cosmic microwave background. Cosmologists typically assume that our observable universe is just the nearby part of a greater entity known as "the universe" where the same physics applies. However, there are several lines of popular but speculative reasoning that assert that even our universe is part of a greater multiverse where either different physical constants occur, different physical laws apply, higher dimensions operate, or slightly different-by-chance versions of our standard universe exist.
Tomorrow's picture: stellar shell game
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Saturday, November 22, 2025
APOD - Dione and Rhea Ring Transit
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit & Copyright: Christopher Go
Explanation: Seen to the left of Saturn's banded planetary disk, small icy moons Dione and Rhea are caught passing in front of the gas giant's extensive ring system in this sharp telescopic snapshot. The remarkable image was recorded on November 20, when Saturn's rings were nearly edge-on when viewed from planet Earth. In fact, every 13 to 16 years the view from planet Earth aligns with Saturn's ring plane to produce a series of ring plane crossings. During a ring plane crossing, the interplanetary edge-on perspective makes the thin but otherwise bright rings seem to disappear. By November 23rd Saturn's rings will have reached a minimum angle for now, at their narrowest for viewing from planet Earth, but then start to widen again. Of course, Dione and Rhea orbit Saturn near the ring plane once every 2.7 and 4.5 days respectively, while the next series of Saturn ring plane crossings as seen from Earth will begin again in 2038.
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Friday, November 21, 2025
APOD - 3I/ATLAS: A View from Planet Earth
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
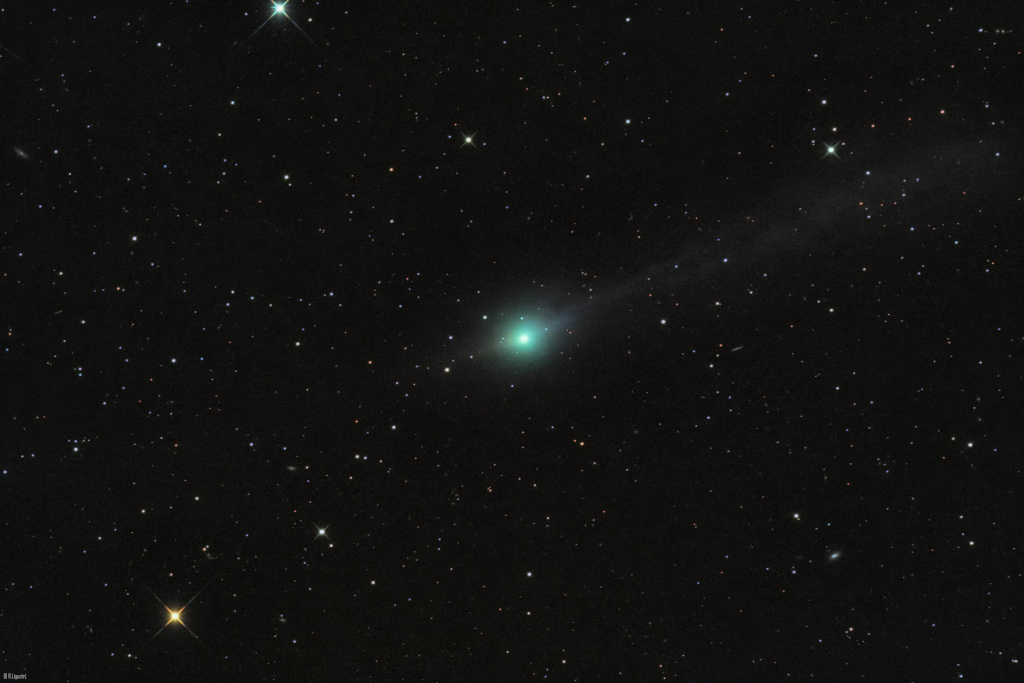
Image Credit & Copyright: Rolando Ligustri
Explanation: Now outbound after its perihelion or closest approach to the Sun on October 29, Comet 3I/ATLAS is only the third known interstellar object to pass through our fair Solar System. Its greenish coma and faint tails are seen against a background of stars in the constellation Virgo in this view from planet Earth, recorded with a small telescope on November 14. But this interstellar interloper is the subject of an on-going, unprecedented Solar System-wide observing campaign involving spacecraft and space telescopes from Earth orbit to the surface of Mars and beyond. And while the comet from another star-system has recently grown brighter, you'll still need a telescope if you want to see 3I/ATLAS from planet Earth. It's now above the horizon in November morning skies and will make its closest approach to Earth, a comfortable 270 million kilometers distant, around December 19.
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Don't forget to pay the tax within 2 days!
I know, it's unpleasant to start the conversation with bad news, but I have no choice.
Few months ago, I have gained access to your devices that used by you for internet browsing.
Afterwards, I could track down all your internet activities.
Here is the history of how it could become possible:
At first, I purchased from hackers the access to multiple email accounts (nowadays, it is a really simple thing to do online).
As result, I could easily log in to your email account (macbud1972.draftpost@blogger.com).
One week later, I installed Trojan virus in Operating Systems of all devices of yours, which you use to open email.
Frankly speaking, it was rather straightforward (since you were opening the links from your inbox emails).
Everything ingenious is quite simple. (o_0)!
My software enables me with access to all controllers inside devices of yours, like microphone, keyboard and video camera.
I could easily download to my servers all your private info, including the history of web browsing and photos.
I can effortlessly gain access to all your messengers, social networks accounts, emails, contact list as well as chat history.
Virus of mine constantly keeps refreshing its signatures (because it is driver-based), and as result remains unnoticed by your antivirus.
Hence, you can already guess why I stayed undetected all this while.
As I was gathering information about you, I couldn't help but notice that you are also a true fan of adult-content websites.
You actually love visiting porn sites and browsing through kinky videos, while pleasuring yourself.
I could make a few dirty records with you in the main focus and montaged several videos showing the way you reach orgasm while masturbating with joy.
If you are still uncertain regarding the seriousness of my intentions,
it only requires several mouse clicks for me to forward your videos to all your relatives, as well as friends and colleagues.
I can also make those vids become accessible by public.
I honestly think that you do not really want that to happen, considering the peculiarity of videos you like to watch,
(you obviously know what I mean) all that kinky content can become a reason of serious troubles for you.
However, we can still resolve this situation in the following manner:
Everything you are required to do is a single transfer of $1370 USD to my account (or amount equivalent to bitcoin depending on exchange rate at the moment of transfer),
and once the transaction is complete, I will straight away remove all the dirty content exposing you.
After that, you can even forget that you have come across me. Moreover, I swear that all the harmful software will be removed from all devices of yours as well.
Make no doubt that I will fulfill my part.
This is really a great deal that comes at a reasonable price, given that I have used quite a lot of energy to check your profile as well as traffic over an extended period of time.
If you have no idea about bitcoin purchase process - it can be straightforwardly done by getting all the necessary information online.
Here is my bitcoin wallet provided below: bc1q28vpq5km7azzcfm097qczyh7n89cl2pjv0psha
You should complete the abovementioned transfer within 48 hours (2 days) after opening this email.
The following list contains actions you should avoid attempting:
#Do not try replying my email (email in your inbox was generated by me alongside with return email address).
#Do not try calling police as well as other security forces. In addition, abstain from sharing this story with your friends.
After I find out (be sure, I can easily do that, given that I keep complete control of all your devices) - your kinky video will end up being available to public right away.
#Do not try searching for me - there is absolutely no reason to do that. Moreover, all transactions in cryptocurrency are always anonymous.
#Do not try reinstalling the OS on your devices or throwing them away. It is pointless as well, since all your videos have already been uploaded to remote servers.
The following list contains things you should not be worried about:
#That your money won't reach my account.
- Rest assured, the transactions can be tracked, hence once the transaction is complete,
I will know about it, because I continuously observe all your activities (my trojan virus allows me to control remotely your devices, same as TeamViewer).
#That I still will share your kinky videos to public after you complete money transfer.
- Trust me, it's pointless for me to continue troubling your life. If I really wanted, I would make it happen already!
Let's make this deal in a fair manner!
Owh, one more thing...in future it is best that you don't involve yourself in similar situations any longer!
One last advice from me - recurrently change all your passwords from all accounts.
Thursday, November 20, 2025
APOD - Alnitak, Alnilam, Mintaka
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit & Copyright: Aygen Erkaslan
Explanation: Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka are the bright bluish stars from east to west (upper right to lower left) along the diagonal in this cosmic vista. Otherwise known as the Belt of Orion, these three blue supergiant stars are hotter and much more massive than the Sun. They lie from 700 to 2,000 light-years away, born of Orion's well-studied interstellar clouds. In fact, clouds of gas and dust adrift in this region have some surprisingly familiar shapes, including the dark Horsehead Nebula and Flame Nebula near Alnitak at the upper right. The famous Orion Nebula itself is off the right edge of this colorful starfield. The telescopic frame spans almost 4 degrees on the sky.
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Wednesday, November 19, 2025
APOD - Chamaeleon Dark Nebulas
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
Image Credit & Copyright: Xinran Li & Houbo Zhao
Explanation: Sometimes the dark dust of interstellar space has an angular elegance. Such is the case toward the far-south constellation of Chamaeleon. Normally too faint to see, dark dust is best known for blocking visible light from stars and galaxies behind it. In this 11.4-hour exposure, however, the dust is seen mostly in light of its own, with its strong red and near-infrared colors creating a brown hue. Contrastingly blue, a bright star Beta Chamaeleontis is visible on the upper right of the V, with the dust that surrounds it preferentially reflecting blue light from its primarily blue-white color. All of the pictured stars and dust occur in our own Milky Way Galaxy with one notable exception: a white spot just below Beta Chamaeleontis is the galaxy IC 3104, which lies far in the distance. Interstellar dust is mostly created in the cool atmospheres of giant stars and dispersed into space by stellar light, stellar winds, and stellar explosions such as supernovas.
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe
Tuesday, November 18, 2025
APOD - The Galactic Plane: Radio Versus Visible
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Discover the cosmos! Each day a different image or photograph of our fascinating universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer.
2025 November 18
Image Credit: Radio: S. Mantovanini & the GLEAM team; Visible: Axel Mellinger (milkywaysky.com)
Explanation: What does the Milky Way look like in radio waves? To better find out, GLEAM surveyed the central band of our galaxy in high resolution radio light as imaged by the Murchison Widefield Array in Australia. As the featured video slowly scrolls, radio light (71 - 231 MHz) is seen on the left and visible light -- from the same field -- on the right. Differences are so great because most objects glow differently in radio and visible light, and because visible light is stopped by nearby interstellar dust. These differences are particularly apparent in the direction toward the center of our galaxy, seen about a third of the way through. Among the many features that appear in the radio, bright red patches are usually supernova remnants of exploded stars, while areas colored blue are stellar nurseries filled with bright young stars.
Tomorrow's picture: the big V
Authors & editors: Robert Nemiroff (MTU) & Jerry Bonnell (UMCP)
NASA Official: Amber Straughn Specific rights apply.
NASA Web Privacy, Accessibility, Notices;
A service of: ASD at NASA / GSFC,
NASA Science Activation
& Michigan Tech. U.
This is an automated email. If you notice any problems, just send me a note at gtracy@gmail.com. You can add and remove email addresses to this distribution list here, https://apodemail.org.Unsubscribe